In the realm of medical diagnostics, endoscopy has emerged as a crucial and versatile tool. This non-invasive procedure allows physicians to peer inside the human body, providing invaluable insights for diagnosis and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of endoscopy, shedding light on its various types, applications, and significance in modern medicine.
Understanding Endoscopy
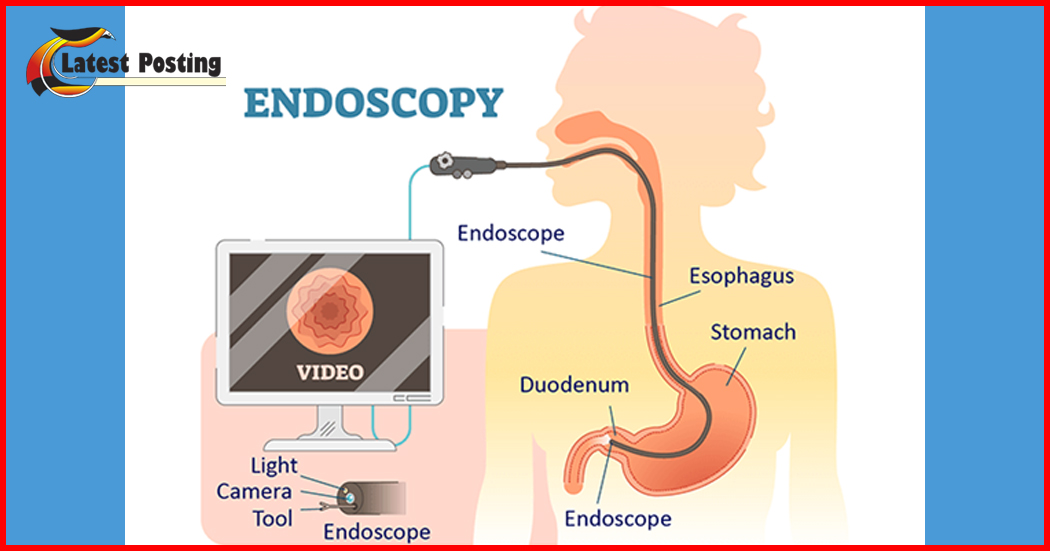
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that involves the use of a thin, flexible tube equipped with a light and camera, known as an endoscope. This instrument allows healthcare professionals to visualize internal organs and structures in real-time. The procedure is commonly used to examine the digestive tract, respiratory system, joints, and other internal organs. Endoscopy plays a pivotal role in diagnosing conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory issues, and joint abnormalities.
Types of Endoscopy
There are several types of endoscopy, each tailored to specific medical needs. Gastrointestinal endoscopy, for instance, explores the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Bronchoscopy focuses on the respiratory system, while arthroscopy is employed for joint examinations. Additionally, there are specialized endoscopic procedures for examining the urinary tract, reproductive organs, and more. The choice of endoscopic procedure depends on the suspected medical condition and the area of the body under investigation.

Applications of Endoscopy
Endoscopy is widely utilized across various medical disciplines due to its versatility. In gastroenterology, it aids in the diagnosis of conditions like ulcers, polyps, and cancers. Pulmonologists use bronchoscopy to investigate respiratory issues, while orthopedic surgeons employ arthroscopy for joint-related concerns. Urologists and gynecologists also benefit from endoscopic procedures to evaluate the urinary and reproductive systems, respectively. The ability to directly visualize internal structures enhances accuracy in diagnosis and facilitates targeted treatment plans.
Advantages of Endoscopy
The advantages of endoscopy extend beyond its diagnostic capabilities. One significant benefit is the minimally invasive nature of the procedure, which often results in shorter recovery times and reduced postoperative discomfort. Additionally, endoscopy allows for real-time imaging, enabling immediate assessment and intervention. This precision contributes to more accurate diagnoses, leading to timely and effective treatment strategies. Patients undergoing endoscopic procedures typically experience fewer complications compared to traditional surgical methods.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the field of endoscopy is evolving with it. Innovations such as capsule endoscopy, which involves swallowing a pill-sized camera, are becoming more prevalent, offering a less invasive alternative for certain examinations. Artificial intelligence is also playing a role in improving endoscopy, aiding in the detection of abnormalities and enhancing diagnostic accuracy. The ongoing development of these technologies promises to further refine and expand the capabilities of endoscopic procedures in the years to come.

how long does an endoscopy take
The duration of an endoscopy procedure can vary depending on the type of endoscopy being performed and the specific circumstances of the individual patient. In general, most endoscopies are relatively quick and typically last between 15 minutes to an hour. However, several factors can influence the time it takes:
- Type of Endoscopy: Different types of endoscopic procedures focus on various areas of the body, such as the digestive tract, respiratory system, or joints. The complexity and extent of the examination will affect the duration.
- Purpose of the Endoscopy: The primary purpose of the endoscopy, whether it’s for diagnostic purposes, surveillance, or treatment, can impact the length of the procedure. For example, therapeutic interventions during endoscopy may take additional time.
- Patient’s Condition: The patient’s health and anatomy play a role. Certain medical conditions or anatomical variations may make the procedure more challenging or time-consuming.
- Preparation: Preparing the patient for the procedure, such as administering sedation, may add to the overall time. The recovery period after the endoscopy is also a consideration.
- Complications or Unexpected Findings: If complications arise during the procedure or if unexpected findings require further investigation or treatment, the duration may be extended.
It’s important to note that while the actual endoscopy procedure itself may be relatively short, patients typically spend additional time in the endoscopy unit for pre-procedure preparation and post-procedure recovery. This ensures the patient’s well-being and allows for monitoring after the sedation wears off.
Patients undergoing an endoscopy should consult with their healthcare provider to get specific information about the expected duration of their particular procedure and any necessary preparations.
endoscopy prep
It preparation is a crucial aspect of the procedure to ensure accurate and successful results while minimizing potential risks. The specific instructions for this preparation can vary based on the type of endoscopy (e.g., upper endoscopy, colonoscopy) and the medical facility’s protocols. Always follow the guidelines provided by your healthcare provider, and here are some general considerations:
1. Communication with Your Healthcare Provider:
- Communicate any existing medical conditions, allergies, or medications you are taking.
- Inform your healthcare provider about any past adverse reactions to sedation or anesthesia.
2. Fasting:
- For most endoscopic procedures, fasting is essential. This usually involves refraining from eating or drinking for a specified period before the procedure.
- Commonly, patients are instructed not to eat or drink anything for at least 6 to 8 hours before the procedure, although these requirements may vary.
3. Medication Adjustments:
- Discuss with your healthcare provider whether you should adjust the schedule or dosage of any regular medications.
- Certain medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be temporarily stopped or adjusted.
4. Bowel Preparation (For Some Procedures):
- For procedures like colonoscopy, a bowel preparation is often required. This involves taking a laxative to cleanse the colon before the examination.
- Follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider regarding the timing and dosage of the bowel preparation.
5. Arrange Transportation:
- Because sedation is often used during this, it’s important to arrange for someone to drive you home afterward.
- Avoid making any important plans or commitments for the rest of the day, as the effects of sedation can linger.
6. Comfortable Clothing:
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing on the day of the procedure. This makes it easier for the healthcare team to place monitoring devices and for you to change into a gown if necessary.
7. Follow-Up Instructions:
- After the procedure, your healthcare provider will provide instructions for the recovery period. This may include dietary restrictions, activity limitations, and any necessary follow-up appointments.
8. Address Concerns:
- If you have any concerns or questions about the procedure or its preparation, don’t hesitate to discuss them with your healthcare provider beforehand.
Always adhere to the specific guidelines provided by your healthcare team, as individual requirements may vary. Following the preparation instructions diligently enhances the safety and effectiveness of the this procedure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, endoscopy stands as a cornerstone in modern medical diagnostics, providing healthcare professionals with a direct window into the human body. Its diverse applications and minimally invasive nature make it an invaluable tool for diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions. As technology continues to propel the field forward, the future of endoscopy holds promise for even more precise and efficient medical examinations. With its ability to significantly impact patient outcomes, it remains at the forefront of medical innovation.
Common FAQs
1. What is an endoscopy?
- An endoscopy is a medical procedure that involves the use of a flexible tube with a light and camera, known as an endoscope, to visualize and examine the interior of the body. It is commonly used to inspect the digestive tract, respiratory system, joints, and other internal organs.
2. Why is an endoscopy performed?
- It is perform for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. It helps in identifying conditions such as ulcers, polyps, tumors, inflammation, and other abnormalities. Endoscopic procedures can also be use for treatments like removing polyps, stopping bleeding, or taking tissue samples for biopsy.
3. Are there different types of endoscopy?
- Yes, there are various types of, each focusing on specific areas of the body. Gastrointestinal endoscopy examines the digestive tract, bronchoscopy looks at the respiratory system, and arthroscopy is use for joint examinations. Other types include cystoscopy for the bladder, hysteroscopy for the uterus, and more.
4. How long does an endoscopy take?
- The duration of an endoscopy varies depending on the type of procedure and individual circumstances. In general, most endoscopies take between 15 minutes to an hour. Factors such as the purpose of the endoscopy, patient’s condition, and any unexpected findings can influence the time.
5. Is sedation use during endoscopy?
- Yes, sedation is often use during it to ensure patient comfort and cooperation. The level of sedation can vary, from mild sedation to general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the procedure. Patients should discuss the sedation plan with their healthcare provider before the procedure.
6. What is the preparation for an endoscopy like?
- Preparation for it typically involves fasting for a certain period before the procedure. For some examinations, such as colonoscopy, bowel preparation with laxatives may be require. Patients may also need to adjust medications and arrange for transportation, especially if sedation is use.
7. Are there risks associate with endoscopy?
- While it is generally consider safe, there are some risks, including bleeding, infection, and perforation. The likelihood of complications is low and varies depending on the type of endoscopy and the patient’s health. Patients should discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider.
8. How soon can I resume normal activities after an endoscopy?
- The recovery time after it depends on the type of procedure and the sedation used. Patients are typically monitor for a short period after the procedure. It is common to experience some drowsiness, and driving or operating heavy machinery is usually restrict for the rest of the day. Patients can usually resume normal activities the next day.
9. Can I eat after an endoscopy?
- After the procedure, patients are usually allow to eat and drink once the effects of sedation wear off. The healthcare provider will provide specific instructions regarding post-procedure diet and activities.
10. Are there alternatives to traditional endoscopy?
- Yes, there are alternatives such as capsule, where a small pill-size camera is swallow to capture images as it passes through the digestive tract. However, the choice of the method depends on the specific diagnostic needs, and not all conditions can be adequately address with alternative methods.





One thought on “Depths of Medical Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Guide to Endoscopy”